Femoroacetabular Impingement
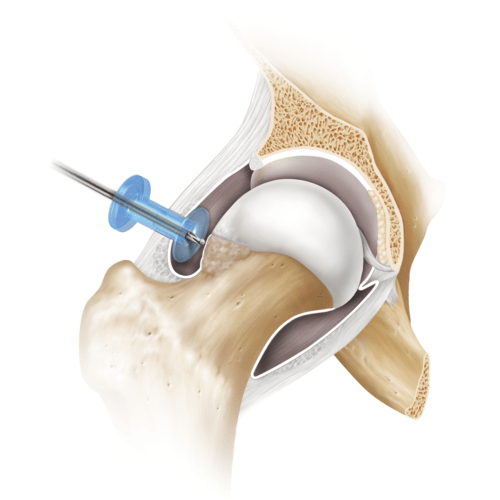
FAI is not true arthritis by definition. However, FAI is overgrowth of bone on either the “ball” (aka – CAM lesion) or “socket” (aka – Pincer lesion). A CAM lesion results is extra bone formation or a bump on the femur (thigh bone) and can impinge on the socket with motion. A Pincer lesion is extra bone formation on the acetabulum (pelvis). When the leg is brought to extreme ranges of motion, it will impinge on the Pincer. A patient with FAI can have an isolated CAM or an isolated Pincer, but most often will have a combination of both types of FAI, causing impingement and ultimately degeneration of the joint cartilage and soft tissue surrounding the joint (labrum).

Causes
FAI is usually a combination of anatomical anomalies and abnormal stresses, typically from sports activities.

Symptoms
FAI causes pain (particularly in the groin), decreased motion and strength. Clicking may also be felt in the hip if the soft tissue around the socket (labrum) is torn in conjunction with the FAI.

Diagnosis
Dr. Chandrasekaran will perform a physical exam and obtain X-rays. Pain with provocative maneuvers will increase pain, leading to the diagnosis of FAI. X-rays will demonstrate extra bone formation on the femur, the acetabulum, or both. Dr. Chandrasekaran may order additional diagnostic tests to evaluate all hip structures (CT/”CAT” scan) to better evaluate the fracture or MRI to evaluate the muscles, tendons and ligaments.
How it is treated?

Non-Operative
Historically, non-operative treatment consisted of rest, anti-inflammatory medication and activity modification. Patients were often advised to “wait until the arthritis got bad enough” before having hip replacement. Current non-operative treatment may include the above treatments with a specific physical therapy program dedicated toward treating FAI.

Operative
Operative treatment of non-arthritic FAI consists of a minimally-invasive hip arthroscopy to treat the underlying pathology. Arthroscopic removal of extra bone on both the femur (aka – osteoplasty) and acetabulum (aka – rim trimming) is performed, as well as repair of any other pathology in and around the hip joint. Labral repair is commonly performed in conjunction with osteoplasty and rim trimming. Hip arthroscopy may delay the onset of hip arthritis. Over time, patients with FAI ultimately continue to progress to arthritis.